Cell Theory (कोशिका सिद्धांत): It states mainly three basic information:
- Living things are composed of one or more Cells,
- The cell is the basic (smallest) unit of life. It is Structural and Functional Unit of Life. &
- Cells arise from existing cells. Its means – Life arise from life.
CELL (कोशिका):
- Many Cells make together ⇒ TISSUE (उत्तक)
- Many Tissues make together ⇒ ORGAN (अंग)
- Many Organs make together ⇒ ORGAN SYSTEM (अंगतंत्र)
- This Organ System is Called ⇒ ORGANISM (BODY)

Types of CELLs:
Cells are of two types: 1. Prokaryotic 2. Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic (प्रोकार्योटिक):
- It do not contains a nucleus.
- Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
- Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life.
- Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth.
- It does not contains Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
- Prokaryotes are the smallest of all organisms having size range from 0.5 to 2.0 µm in diameter.
- The DNA of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single circular chromosome.
- The nuclear region in the cytoplasm is called the nucleoid.
Eukaryotic (यूकैरियोटिक):
- It contains a nucleus.
- Plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, algae etc. all are examples of eukaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotes can be either single-celled or multicellular.
- It may contains one to several thousand Mitochondria.
- Algae and Plant’s Eukaryotic cell consists Chloroplasts in it.
- The DNA of a Eukaryotic cell consists of one or more linear molecules, called chromosomes, which are associated with histone proteins.
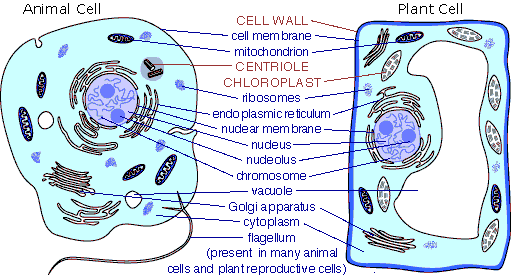
Some Important Terms for Cell Structure:
- Cell Structure has a big theory. Here we will discuss only some important term for cell structure which are important for exams point of view. Please have a look:
Cell nucleus (कोशिकीय केंद्रक): It is a cell’s information center, so it is called ‘Brain of Cell.’ A nucleus is the mostly found in a eukaryotic cell. It houses the cell’s chromosomes, and is the place where almost all DNA replication and RNA synthesis occur. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins.
Ribosomes (राइबोसोम): Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. The ribosome is a large complex of RNA and protein molecules where RNA from the nucleus is used to synthesis proteins from amino acids. During protein synthesis, ribosomes assemble amino acids into proteins.
Mitochondria (माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया): It generate energy for the cell, so Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Respiration occurs in the cell mitochondria, which generate the cell’s energy by oxidative phosphorylation, using oxygen to generate ATP.
Mitochondria contain their own ribosomes and DNA; combined with their double membrane.
Enzyme (एंजाइम): It is globular protein that catalysis a biological chemical reaction.
Lysosomes (लाइसोसोम): It is suicide bag of a cell. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes (acid hydro-lases). They digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria.
Cell wall (कोशिका भित्ति): The cell wall acts to protect the cell mechanically and chemically from its environment, and is an additional layer of protection to the cell membrane. Different types of cell have cell walls made up of different materials:-
- Plant cell walls are primarily made up of Cellulose,
- Fungi cell walls are made up of Chitin.
- Bacteria cell walls are made up of Peptidoglycan.
Chlorophyll (क्लोरोफिल): It is a green photosynthetic pigment found in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyll absorbs mostly in the blue and lesser in the red portions of the electromagnetic spectrum, hence its intense color is green.
Chloroplasts (क्लोरोप्लास्ट): Chloroplasts can only be found in plants and algae so it generate energy for their cells. They capture the sun’s energy to make carbohydrates through photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts (वर्णीलवक): These are colored plastids which found in fruits, flowers, roots, and leaves. Chromoplasts is reason for the color of these plant organs. Chromoplasts colored due to the pigments that are produced and stored inside them.
Note:
- Animal cells have a Centrosome and Lysosomes while plant cells do not.
- Plant cells have a Cell wall, Chloroplasts and other specialized plastids, whereas animal cells do not.
Important Facts of Cell for Exams :
- Smallest Unit of Life – Cell
- Structural and functional unit of Life – Cell
- Study of Cell is Called – Cytology (कोशिका का अध्ययन).
- Cell word is given by – Robert Hooke (रॉबर्ट हुक)
- Cell Theory was given by – Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
- First cell Discovered was – Dead Cell (मृत कोशिका).
- It was from – Cork Tissue (पेड़ की छाल से)
- First living cell was discovered by – Anton Van Leeuwenhoek.
- First living cell was a Plant Cell – Cell of Onion (प्याज की कोशिका)
- Smallest cell is a bacteria cell – Mycoplasma Gallisepticum (MG) (माइकोप्लाज्मा गैलिस्पेक्टाम)
- Largest cell on Earth is – Ostrich Egg (शुतुरमुर्ग का अंडा)
- Longest cell in Human body – Cell of Neuron System/ Brain Cell.
- Power House of the cell – Mitochondria (माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया).
- Kitchen of Plant Cell is – Chlorophyll (क्लोरोफिल)
- Brain of a Cell is – Nucleus (केंद्रक)
- Suicide bag of a cell – Lysosomes (लाइसोसोम)
- Who is responsible for the color of Fruits and Flowers : Chromoplasts (वर्णीलवक)
- Green color of plants is due to : Chlorophyll (क्लोरोफिल)
- Platform for ‘Protein Synthesis’ in cell is : Ribosomes (राइबोसोम)




